Thermoforming machines are at the forefront of modern manufacturing, offering versatile solutions for shaping plastics into various forms. This article explores how these machines work, their applications across industries, and the trends driving their evolution, such as sustainability and automation.
What Are Thermoforming Machines?
Thermoforming is a manufacturing process where a plastic sheet is heated to a pliable temperature and shaped over a mold to create the desired product. This process leverages the unique properties of thermoplastics, which can be reheated and reshaped multiple times, making it a highly efficient and adaptable method.
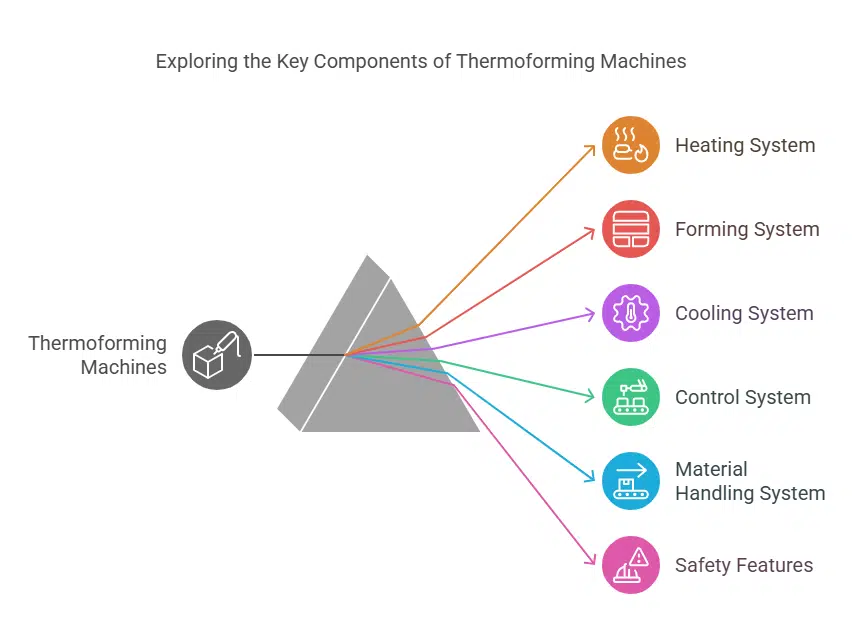
Key Components of Thermoforming Machines
Thermoforming machines consist of three critical components that ensure seamless production:
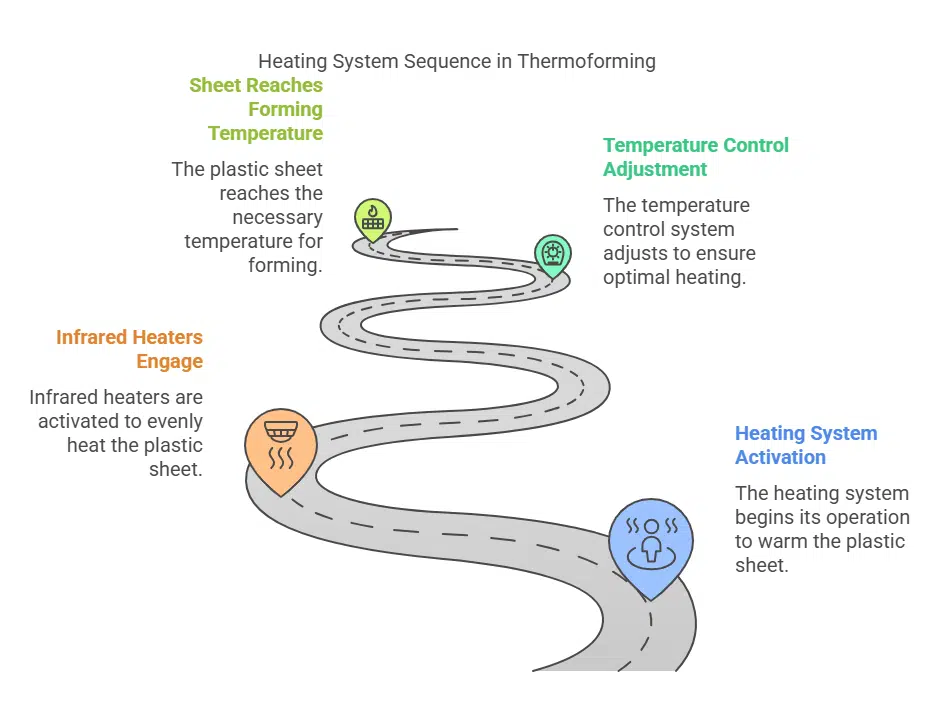
- Heating System: Prepares the plastic sheet by raising it to the required temperature for forming.
- Forming Station: Contains molds that define the shape and dimensions of the product. The plastic sheet is pressed against the mold, taking its precise shape.
- Cooling System: Solidifies the product for quick turnaround and ensures it retains its structure during mass production.
This streamlined process allows manufacturers to achieve high production rates and consistent quality across a wide range of applications.
Applications Across Industries
Thermoforming is widely used in various industries due to its adaptability and efficiency. Some key applications include:
Packaging
- Thermoforming is essential in creating blister packs, clamshell containers, and valve-sealed containers. These products not only protect goods but also enhance shelf appeal through innovative designs.
Automotive
- The automotive sector relies on thermoforming to produce lightweight, durable components such as dashboards, interior panels, and exterior trims. These parts contribute to reducing vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency.
Consumer Goods
- Everyday items like trays, containers, and appliance components are efficiently produced using thermoforming machines, meeting consumer demands for high-quality, cost-effective products.
Advantages of Thermoforming Machines
Thermoforming offers several benefits compared to other manufacturing methods, such as injection molding:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Ideal for both small and large production runs without significant financial investment, making it accessible for start-ups and businesses testing prototypes.
- Material Efficiency: Thermoforming minimizes waste by using a variety of thermoplastic materials, many of which are recyclable.
- Rapid Production: Thermoforming machines operate at high speeds, allowing manufacturers to meet growing market demands quickly.
- Flexibility: The ability to produce a wide range of shapes and sizes makes thermoforming suitable for diverse applications.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices in Thermoforming
As sustainability becomes a key focus, thermoforming is evolving to support eco-conscious manufacturing. Innovations in materials and processes include:
- Recycled Plastics: Incorporating post-consumer or industrial recycled plastics into production reduces environmental impact.
- Design for Recyclability: Products are being designed with end-of-life recycling in mind, minimizing landfill waste.
- Energy-Efficient Operations: New machines optimize energy consumption, reducing carbon footprints.
These practices not only benefit the environment but also align with consumer and regulatory expectations for greener production methods.
Future Trends in Thermoforming Technology
The thermoforming industry is poised for transformation, driven by these emerging trends:
Automation and AI Integration
- Automated systems enhance precision, reduce labor costs, and improve efficiency. With robotics and AI, thermoforming processes can be managed with minimal human intervention, boosting productivity and consistency (Subramanian, 2024).
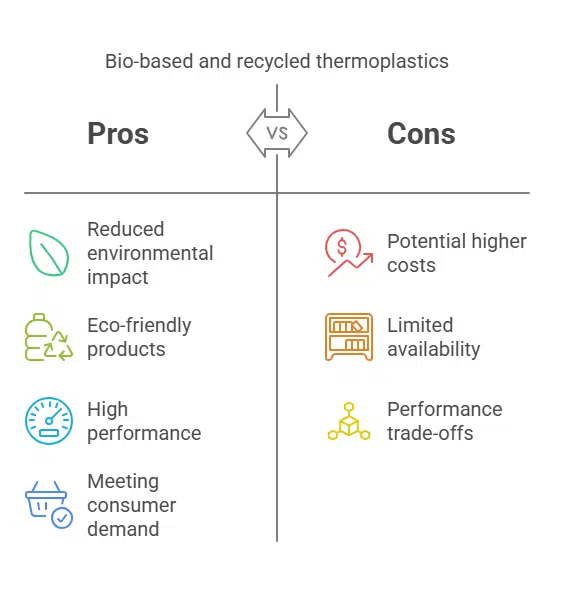
Innovative Materials
- Advancements in bio-based and recycled thermoplastics allow manufacturers to create sustainable products without compromising on quality or durability (Klein, 2022).
Digital Monitoring and IoT
- Smart systems equipped with sensors and IoT capabilities enable real-time monitoring of machine performance, minimizing downtime and optimizing production workflows.
Conclusion
Thermoforming machines have revolutionized manufacturing by offering efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable solutions for a variety of industries. From packaging to automotive components, these versatile machines play a critical role in modern production. As automation, AI, and sustainable practices continue to shape the industry, thermoforming will remain a cornerstone of innovative manufacturing.
Call to Action:
Interested in learning more about how thermoforming machines can transform your production process? Contact us today or download our free guide on sustainable thermoforming practices!
FAQs About Thermoforming Machines
A variety of thermoplastics, such as PET, PVC, polystyrene, and polycarbonate, can be used depending on the application. Many of these materials are recyclable.
Thermoforming is more cost-effective for small production runs and is ideal for creating larger parts. Injection molding, on the other hand, is better suited for high-volume production of intricate designs.
Yes, thermoforming supports sustainability by using recycled materials and optimizing designs for recyclability. Advances in energy-efficient machines further reduce environmental impact.
Citations and References
- Engelmann, Sven. Advanced Thermoforming: Methods, Machines and Materials, Applications, Automation, Sustainability, and the Circular Economy, 2024.
- Gruenwald, Geza. Thermoforming: A Plastics Processing Guide. Routledge, 2018.
- Throne, Jim. Thermoforming. In Applied Plastics Engineering Handbook, pp. 449-480. William Andrew Publishing, 2024.
- Owusu-Akyaw, Akwasi. Design and Manufacturing of a Benchtop Thermoforming Machine. PhD diss., MIT, 2024.
- Subramanian, Muralisrinivasan Natamai. Thermoforming Processing and Technology. John Wiley & Sons, 2024.
- Klein, Peter. Fundamentals of Plastics Thermoforming. Springer Nature, 2022.



